Generator reference
This reference goes through all available model elements as well as their properties, describing what the generator does with this information and which things are still missing in the created implementation. Also it shows which artifacts are created from which model elements.
Most screenshots in this section are taken from the example application called RecipeManager.
Describing behavioural aspects
As Zikula uses Symfony and the Doctrine ORM layer, the data layer in ModuleStudio allows to precisely express the different concepts and available functions. For example you can use a huge amount of validation constraints and special field types.
From each entity in the data layer there are entity classes and repository classes created. Therewith the contained fields as well as their properties are accordingly reflected. For many data types and basic properties, like unique, readonly or notnull this happens with a one to one adaption. Several things are shortened for convenience in ModuleStudio though. Furthermore there are some additional data types, like for example for users, email addresses, urls and file uploads. An email field is treated by the generator as a string field in Doctrine which has the email validator activated.
Validators are generally not explicitly written in MOST, but simply defined using properties. So there are for example attributes like ipaddress for string fields or past and future for date and time fields.
The different types of relations in Doctrine are all offered, too. For inheritance relationships the strategy can be selected (single table, joined). All other connection types store a name for the two entities on both sides (source alias and target alias) as well as the referenced fields (source field and target field). Because the primary id fields of entities are not part of the model, but automatically added before the generation, the string id is allowed and also set per default. By changing these fields it is possible to describe also relations referencing other fields. Beside this it is possible to have multiple relationships between the same entities and also self relations, as long as their alias settings are unique. Finally you can also define how the cascading behaviour should look like, again supporting all options offered by Doctrine.
The ModuleStudio DSL also supports several behavioural extensions for Doctrine, like for example trees, translatable fields, slugs and loggable entities. There are also some Zikula-specific additions by the way, like Categorisable.
Event listeners or subscribers are not explicitly described in the models, but some base implementations are already generated though which can be implemented in the empty subclasses if needed.
Application layer
Language elements
Named object
This is the common base class of almost all model elements.
It includes the following properties:
- name - The name of the element.
- documentation - A description for documenting the element.
Documentation is used in several places of generated applications. For example if any documentation is defined for an entity this will be shown right after the heading of the corresponding index template. So you could for example add a description for the person entity explaining what persons are and what information they store. If a user then navigates to the persons list he knows immediately what he is looking at. Documentation for single fields is used in editing forms to provide additional help.
In general documentation entries are generated as Translator calls to support translations. For example This is a test. results in {% trans %}This is a test.{% endtrans %}. For entities there is also a special expert feature available: you can use Twig variables in the documentation field. So These are {{myVar}} and {{ otherVar }}. results in {% trans with {'%myVar%': myVar|default, '%otherVar%': otherVar|default} %}These are %myVar% and %otherVar%.{% endtrans %}.
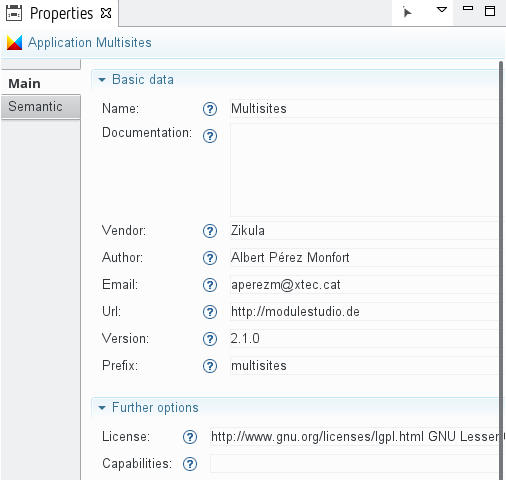
Application
Represents an application described by the model.
It includes the following basic properties which are mainly, but not only used to create meaningful file headers:
- vendor - The vendor of the application. Usually this is the name of a company or institution. The vendor and name of an application are combined to a unique name. This makes it possible to have for example multiple
Newsbundles installed from different vendors. - author - The author of the application. Usually this is the full name of the developer.
- email - The email address of the developer.
- license - The license of this application. Defaults to LGPL. If either GPL or LGPL are used the generator creates corresponding license files, too.
- prefix - A prefix for all database tables of this application. Will be used in entity classes.
- url - The homepage of the developer.
- version - The application version. Must conform to the pattern
x.y.z- for example1.0.0which is also the default value. Will be used in the composer file of the created application.
An application may furthermore have the following references:
- entities - Allows referencing one or more data objects.
- relations - Allows referencing one or more relationships.
- variables - Allows referencing one or more variables.
In addition, an application can configure several further properties to customise generator settings. You can control which features should be generated and take influence on some behavioural aspects of the generator.
- symfonyVersion - The targeted Symfony version. See below.
- generateAccountApi - A boolean specifying whether account panel integration should be generated or not. Default value is
true. - generateRssTemplates - A boolean specifying whether RSS index templates should be generated or not. Default value is
true.
- generateAtomTemplates - A boolean specifying whether Atom index templates should be generated or not. Default value is
true.
- generateCsvTemplates - A boolean specifying whether CSV index templates should be generated or not. Default value is
true. - generateXmlTemplates - A boolean specifying whether XML index and detail templates should be generated or not. Default value is
true.
- generateJsonTemplates - A boolean specifying whether JSON templates should be generated or not. Default value is
true.
- generateKmlTemplates - A boolean specifying whether KML templates should be generated or not. Requires geographical flag on corresponding entities. Default value is
true. - generateIcsTemplates - A boolean specifying whether ICS (iCalendar) templates should be generated or not. Requires start date and end date fields on corresponding entities. Default value is
true. - generatePdfSupport - A boolean specifying whether support for exporting PDF files should be generated or not. Default value is
false. - generateOnlyBaseClasses - A boolean specifying whether only base classes should be generated. May be useful for doing simple upgrades without structural changes. Default value is
false. - skipFiles - Comma-separated blacklist with each entry representing a file path which should not be generated. The file pathes are relative from the application’s root folder, for example
Resources/views/Person/detail.html.twig. Default value is an empty string. - markFiles - Comma-separated list with file pathes which should be marked by special file names. The file pathes are relative from the application’s root folder, for example
Resources/views/Person/detail.html.twig. Instead of the original name each file is generated using the patternfilename.generated.extension. This setting can be useful for doing bigger merges comparing the generated version with a customised one. Default value is an empty string. - timestampAllGeneratedFiles - A boolean specifying whether the generated by message should contain a timestamp in all files or only in the Bootstrap file. Default value is
false. - versionAllGeneratedFiles - A boolean specifying whether the generated by message should contain the ModuleStudio version in all files or only in the Bootstrap file. Default value is
true. - generatePoweredByBacklinksIntoFooterTemplates - A boolean specifying whether generated footer templates should contain backlinks to the ModuleStudio website. Default value is
true. - generateTests - A boolean specifying whether test cases should be generated or not. Default value is
true. At the moment only some stubs are created though (see generator issue #6 on GitHub). - writeModelToDocs - A boolean specifying whether the model file and it’s diagram image are written into the application’s docs folder or not. Default value is
true. - generateTechnicalDocumentation - A boolean specifying whether stand-alone HTML files with technical documentation should be generated or not. Default value is
true. At the moment two reports are generated: structural overview and technical complexity - both in English and German. - indexActionsPosition - Allows to specify whether and where item actions should be available on index pages. Default value is
START. Available options are explained below. - indexActionsStyle - Allows to specify the style used by the included item actions on index pages. Default value is
DROPDOWN. Available options are explained below. - indexActionsWithIcons - A boolean specifying whether item actions on index pages should contain an icon in addition to their label or not. Default value is
true. - detailActionsPosition - Allows to specify whether and where item actions should be available on detail pages. Default value is
START. Available options are explained below. - detailActionsStyle - Allows to specify the style used by the included item actions on detail pages. Default value is
DROPDOWN. Available options are explained below. - detailActionsWithIcons - A boolean specifying whether item actions on detail pages should contain an icon in addition to their label or not. Default value is
true.
Symfony version
Specifies the Symfony version for which the application should be generated.
Can be one of the following options:
SF71- Targets the last Symfony 7.1.x version.SF70- Targets the last Symfony 7.0.x version. This is the default value.
Item actions position
Specifies the placement of item actions.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- No item actions are available at all.START- Default value. Item actions are included at the beginning, for example in the first table column on index pages or the top area on detail pages.END- Item actions are included at the end, for example in the last table column on index pages or the bottom area on detail pages.BOTH- CombinesSTARTandEND. Only allowed for detail pages.
Item actions style
Specifies the style used for item actions.
Can be one of the following options:
LINK- Normal links/anchors with a label and optionally an icon.ICON- Normal links/anchors with an icon only (no label, but tooltips).BUTTON- Links/anchors styled as buttons with a label and optionally an icon.BUTTON_GROUP- Links/anchors styled as a button group with a label and optionally an icon.DROPDOWN- Default value. A drop-down menu containing normal links/anchors with a label and optionally an icon.
For all options except ICON the links contain a label and optionally an additional icon (depending on the withIcons flags).
Data layer
The data layer in ModuleStudio has been designed for a precise description of entities and associations. To understand all the elements and properties please read the Doctrine 2 documentation before.
Language elements
Data object
This abstract class collects properties which are shared by mapped superclasses and entities.
A data object has no properties, but may have the following references:
- application - Reference to the owning element.
- fields - Allows referencing one or more fields.
Mapped superclass
Represents a mapped superclass like described here.
A mapped superclass has no properties or references in addition to the common data object settings.
Entity
Represents an entity in the data layer which is mapped to a database table.
It has the following properties:
- actions - Allows referencing one or more actions.
- categorisable - A boolean specifying whether this entity should have categories or not. If set to
truethe generator creates an additional entity for managing the categories. During edit actions it is possible to select a desired category. This category will also be shown again on detail pages and in quick navigation forms of index pages. Generated applications also support filtering by categories as well as multiple category registries / properties / trees, however the implementation uses onlyMainper default. Also category-based permissions are supported. Note that if you activate thecategorisableproperty for an entity the generated installer relies on that you did not remove the default categories of Zikula. - categorisableMultiSelection - A boolean specifying whether multiple categories can be selected or not.
- changeTrackingPolicy - How change detection is being done (see below). The default value is
DEFERRED_IMPLICIT. - deleteExpired - Whether obsolete data should be automatically deleted. Requires a datetime field which has been designated as end date. The default value is
false. See also hasArchive below if you want to use archiving instead of deletion. - displayPattern - Pattern for displaying instances of this entity. With the display pattern you can specify arbitrary expressions which are used as textual representation for instances of this entity. For most cases you may want to declare just one field, which is done like
#title#. A more complex example would be#lastName#, #firstName# (#age# years). Of course all fields must exist in the entity with exactly the names used within the display pattern. - geographical - A boolean specifying whether the geographical extension is used or not. If set to
truethe generator will create two additional fields namedlatitudeandlongitude. Also it will consider them in all important application areas and provide an export for the kml format (ifgenerateKmlTemplatessetting has not been set tofalse). During the creation of a new entity with geographical support a nice geolocation feature can be used to ask the user for his current location (this needs to be activated in the application settings though; in addition you need to use HTTPS to make this work in most browsers). Also there is an included integration of the Leaflet library allowing you to utilise comprehensive map interaction functionality in your application.
- hasArchive - Whether the workflow should include an archived state with automatic archiving. Requires a datetime field which has been designated as end date. See workflow types for more information. The default value is
false. See also deleteExpired above if you want to use deletion instead of archiving. - hasTray - Whether the workflow should include a suspended state. See workflow types for more information. The default value is
false. - identifierStrategy - Whether and which identifier strategy is applied. The default value is
AUTO. - leading - A boolean specifying whether this is the primary (and default) entity or not.
- lockType - Whether and which locking strategy is applied. The default value is
NONE. - loggable - A boolean specifying whether the Loggable extension for tracking changes and managing versions is used or not. If loggable is activated the DSL will also require adding a
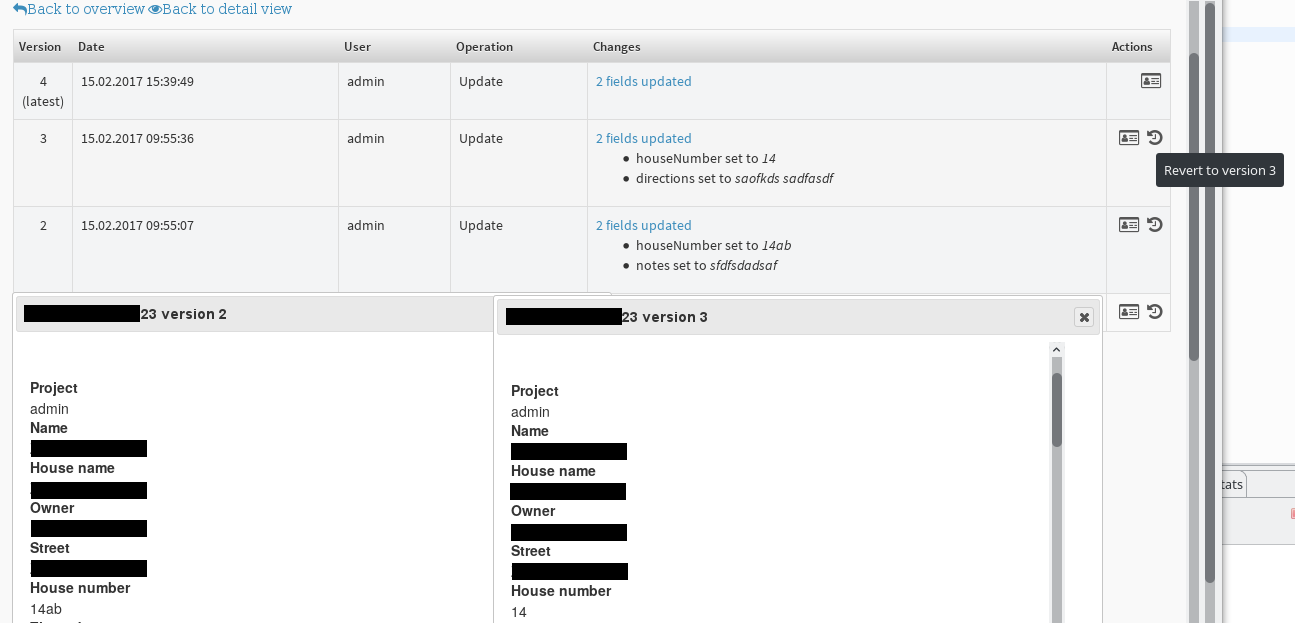
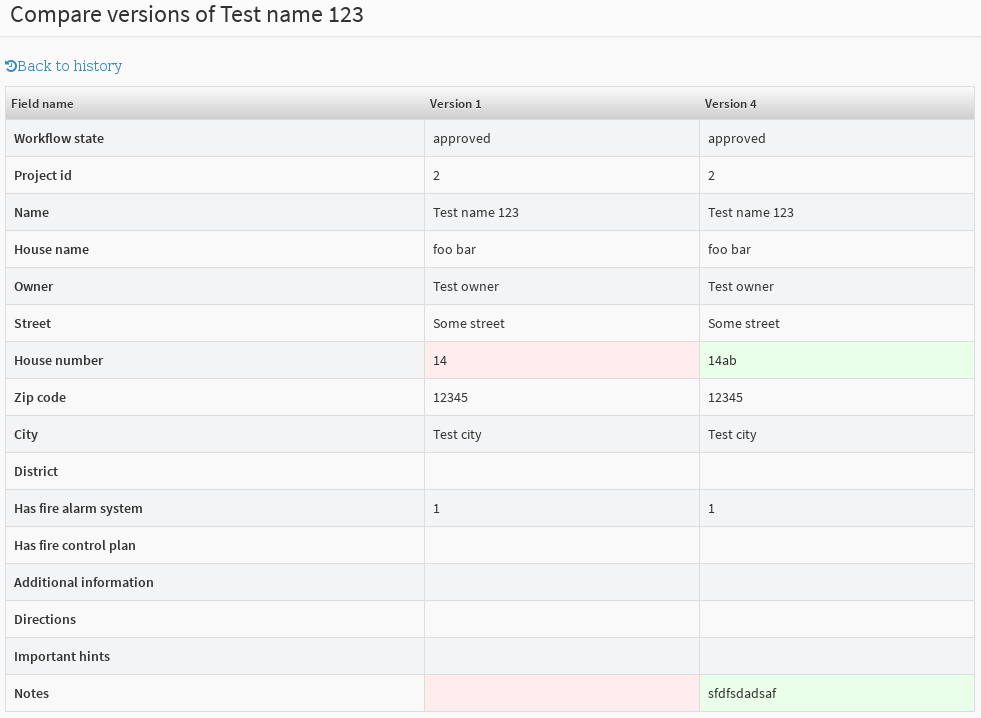
versionfield and optimistic locking because it is handy to have the current version stored in the entity directly. The generator will create an additional entity for managing the log entries if set totrue. Furthermore there is a history page generated which will be available as soon as more than one version of an entity exists. On this history page changes are shown for each version. If the entity has a detail action there is a preview link to display each version. You can also preview multiple versions at the same time and arrange the windows next to each other for easy comparison. Also there are functions to revert an entity to a previous version and to compare different versions using a diff view. Finally if there are deleted entities there is a possibility to inspect and undelete them.
- nameMultiple - Plural form of the name. The generator uses this for collections, list views and other areas where multiple entities are used.
- onAccountDeletionCreator - Controls how an app should change the creator when users are deleted. Only relevant if
standardFieldsis enabled. Default value isADMIN. The available options are listed here. - onAccountDeletionLastEditor - Controls how an app should change the last editor when users are deleted. Only relevant if
standardFieldsis enabled. Default value isADMIN. The available options are listed here. - ownerPermission - Whether users should be able to manage and edit their own data. Defines also whether the workflow should include a deferred state. See workflow types for more information. The default value is
false. IfownerPermissionis enabled the edit permission level allows editing and deleting only for “own” content. For editing also content from other users at least the add level is required then. In addition, the generator creates configuration options which allow to enable a private mode. This extends the owner-based filter also to viewing and accessing data. So with the private option enabled, every user may only see his own data. - readOnly - A boolean specifying whether this entity is read only or not. If set to
truecreating new entities will still be possible, but not editing them. - slugLength - Length of slug field. Defaults to
190. An entity is sluggable as soon as at least one of its fields has setsluggablePositionto a value greater than0. Depending on thetreesetting (explained below) and existing relationships slug support will automatically be extended to utilise tree slug handlers or relative slug handlers. Relative slugs will only be used for now if both entities (connected by the corresponding relationship) have sluggable fields. If there are multiple relationships found where both sides are sluggable the first one will be used for each direction (relative slug handler vs. inversed relative slug handler). - slugSeparator - Separator which will separate words in slug. Default value is
-like in Zikula, too. - slugStyle - Which slug style is used. Default value is
LOWERCASE. - slugUnique - A boolean specifying if the slug is unique or not. Default value is
true. - slugUpdatable - A boolean specifying if the slug can be changed or not. Default value is
true. - tree - Whether and which tree strategy is applied. Default value is
NONE. More information about what the generator creates for trees can be found in the the section about tree types.
- standardFields - A boolean specifying whether the standard fields extension is used or not. If set to
truethe entity will get four additional fields for storing the id of the user who created the item (createdByjoin toUserEntity), the id of the user who did the last update (updatedByjoin toUserEntity), as well as the creation and update dates (createdDateandupdatedDate). This information will be included on detail and edit actions. - workflow - The workflow which is applied to this entity. The default value is
NONE. See workflow types for more information.
An entity has the following references in addition to the common data object settings:
- indexes - Allows referencing one or more indexes.
Field
Represents a field in the data layer.
This base class has the following children at the moment:
- Derived fields correspond to normal columns which are stored in a database.
- Calculated fields correspond to fields which can calculate their values based on other fields.
A field may have the following references:
- cssClass - Optional specification of arbitrary css classes, used for edit pages. Possible example value is
col-sm-6 col-lg-5 col-xxl-3. - entity - Reference to the owning data object.
- varContainer - Reference to the owning variable container.
- visibleOnIndex - Whether the field is shown on index pages or not. The default value is
true. - visibleOnDetail - Whether the field is shown on detail pages or not. The default value is
true. - visibleOnNew - Whether the field is shown on edit pages for new entities (entity creation forms) or not. The default value is
true. - visibleOnEdit - Whether the field is shown on edit pages for existing entities (entity editing forms) or not. The default value is
true. - visibleOnSort - Whether the field can be used for sorting on index pages or not. The default value is
true.
In the following sections all field types are explained in detail. Note that not all properties have an effect if a field is added to a variable container. For example several Doctrine extensions, like tree or translatable, work only with entities and not with variables.
Derived field
Represents a field in the data layer which is mapped to a database column. A derived field comes straight from the data source.
A derived field has the following properties in addition to the common field settings:
- dbName - Name of the database column represented by this field. The default value is an empty string which means that the field name is used for the column, too. This property is primarily interesting for avoiding changes in the database schema when migrating legacy apps.
- defaultValue - The default value of the field. This default value is used when instantiating a new entity instance, for example for creating new entities with the edit action.
- mandatory - A boolean specifying whether this field is mandatory or not. The default value is
true. - nullable - A boolean specifying whether the field may be null or not. The default value is
false. A nullable field may not be mandatory at the same time. - primaryKey - A boolean specifying whether this is a primary key field or not. Default value is
false. Usually there is no need to enable this for any fields as the generator adds primary and foreign key fields automatically. - readonly - A boolean specifying whether this a read only field or not. The default value is
false. If set totruethen this field may not be changed during editing. - sortableGroup - A boolean specifying whether this field acts as grouping criteria for the Sortable extension. The default value is
false. - translatable - A boolean specifying whether this field is translatable or not. The default value is
false. If at least one field in an entity is translatable the generator creates an additional class for managing the translation entities (see Translatable extension for more details). Overall support for translations in the application should get you started. For customisation you can overrideTranslatableHelpermethods.
- unique - A boolean specifying whether this field is unique or not. The default value is
false. If set totruethen an additional validator cares for enforcing the unique constraint on client and server side.
All fields are implemented as entity class member vars. The following sections will look at the different field types in detail.
Calculated field
Represents a field which can dynamically compute it’s value based on other fields.
A calculated field may have the following references in addition to the common field settings:
- operands - Allows referencing one or more derived fields.
Calculated fields are not part of the model editor yet and will therefore be ignored by the generator.
Boolean field
Represents a field type for storing boolean values.
A boolean field has the following properties in addition to the common derived field settings:
- ajaxTogglability - Boolean indicating whether it is possible to switch this flag with ajax or not. If set to
trueall index and detail pages will contain corresponding links instead of only simple state images.
The generator will treat boolean values as checkbox input elements in edit pages. For the output in index and detail templates the yesno modifier is used to show an image indicating the boolean value (green check or red cross).
Abstract integer field
Represents an abstract integer field for grouping different implementations of this field type.
An abstract integer field has the following properties in addition to the common derived field settings:
- length - The length of this field. This controls whether the Doctrine mapping type will be
integer(5-11),bigint(> 11) orsmallint(< 5). Default value is11. - sortablePosition - A boolean specifying whether this field stores the position for the Sortable extension or not. If set to
truethis field will be used as default sorting criteria. In index pages there is a drag n drop functionality offered for easy reordering.
Integer field
Represents a field type for storing integer numbers.
An integer field has the following properties in addition to the common abstract integer field settings:
- aggregateFor - Aggregate field: one-to-many target alias and field name (syntax:
views.amount) which causes the generator creating special methods for aggregation. More information can be found in this article. - counter - A boolean whether this field should act as a counter. Default value is
false. If set totrueand the owning entity has a detail action each view of the detail page will be counted. This property can ideally be combined withdefaultValue "0", mandatory false, visibleOnNew false, visibleOnEdit false. - maxValue - Maximum value. If set to a value other than
0then a validator will enforce this constraint on client and server side. - minValue - Minimum value. If set to a value other than
0then a validator will enforce this constraint on client and server side. - percentage - A boolean specifying whether this field represents a percentage value or not. Default value is
false. - range - A boolean specifying whether this field represents a range or not. Default value is
false. In edit forms a range field is represented as a slider. - unit - An optional field unit which will be used in both edit forms and detail pages. For example a field named
effortcould use aunitnamedhours. Units will be translated. - version - A boolean specifying whether this field should act as a version. Default value is
false. If set totruethe owning entity will need to use optimistic locking. If you need to track changes and manage versions you also need to activateloggablefor the corresponding entity.
In edit pages the generator will use integer input elements as well as validation on client and server side. For the output in index and detail templates the value will just be shown.
Number field
Represents a field type for storing decimal and floating numbers.
A number field has the following properties in addition to the common derived field settings:
- aggregationField - A boolean specifying whether this field should act as an aggregate field. Default value is
false. If set totruethe generator creates special methods for aggregation. More information can be found in this article. - currency - A boolean specifying whether this field should be treated as currency. Default value is
false. If set totruethe generator will use thelocalizedcurrencyfilter instead oflocalizednumberduring output. - length - The length of this field. Default value is
10. - maxValue - Maximum value. If set to a value other than
0then a validator will enforce this constraint on client and server side. - minValue - Minimum value. If set to a value other than
0then a validator will enforce this constraint on client and server side. - numberType - Allows to define the number type for this field. Default value is
DECIMAL. The available options are explained below. - percentage - A boolean specifying whether this field represents a percentage value or not. Default value is
false. - scale - The amount of digits after the dot. Default value is
2. - unit - An optional field unit which will be used in both edit forms and detail pages. For example a field named
effortcould use aunitnamedhours. Units will be translated.
In edit pages the generator will use number input elements as well as validation on client and server side. For the output in index and detail templates the value will just be shown using a formatting filter.
Number field type
Represents different types for a number field.
Can be one of the following options:
DECIMAL- Default value. Represents a decimal number.FLOAT- Represents a floating number.
Abstract string field
Represents an abstract string field for grouping different implementations of this field type.
An abstract string field has the following properties in addition to the common derived field settings:
- fixed - A boolean specifying whether this field has a fixed length or not. Default value is
false. - minLength - Minimum length. If set to a value other than
0then a validator will enforce this constraint on client and server side. - regexp - Regular expression to validate against. Possible example values are
/^\w+/and/\d/. - regexpOpposite - A boolean specifying the logical way of checking
regexp. Default value isfalse. If set totruethen validation will pass only if the given string does not match the pattern.
If one of these properties is set to true a corresponding validator will check this constraint on client and server level.
- sluggablePosition - Position of this field in the created slugs. A value of
0(default) means that this field is not part of the slug at all. If at least one field in an entity has a sluggable position greater than0then this entity is considered as sluggable. In this case a permalink is built automatically from all fields in ascending position. See the slug properties on entity level for slug-related configuration options.
String field
Represents a field type for storing string values.
A string field has the following properties in addition to the common abstract string field settings:
- isbn - Allows to define whether this field represents a number in ISBN (International Standard Book Number). Default value is
NONE. You can choose from different validation options. - issn - Allows to define whether this field represents a number in ISSN (International Standard Serial Number). Default value is
NONE. You can choose from different validation options. - ipAddress - Allows to define whether this field represents an IP address. Default value is
NONE. You can choose the covered ip address scope. - ipTraceable - Which ipTraceable type is used. Default value is
NONE. - ipTraceableChangeTriggerField - Optional name of field to use as change trigger (if type is
CHANGE. Can also beworkflowStateor the name of an incoming relation (syntaxsourceAlias.field). - ipTraceableChangeTriggerValue - Optional value of field to use as change trigger (if type is
CHANGE). - length - The length of this field. Default value is
255. - role - Allows to define a semantic role for this field. Default value is
NONE. The available options are explained below. - unit - An optional field unit which will be used in both edit forms and detail pages. For example a field named
effortcould use aunitnamedhours. Units will be translated.
In edit pages the generator will use single-line input elements for string fields - except you defined something else (using options like role or isbn). Other validations are added together and applied as well.
String role
Represents different semantic roles a string field can have.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- Default value. Means that the corresponding string field just represents a string without special semantic.BIC- A BIC (business identifier code).CIDR- CIDR (classless inter-domain routing).COLOUR- A CSS colour code (different formats allowed). A colour picker is used in edit pages for convenient selection of colour codes.COUNTRY- A ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code. A country selector is used in edit pages. For the output in index and detail templates an output modifier is used to display the full country name instead of the unreadable country code. If the field is notmandatorythe edit selector provides a placeholder entry named All.CREDIT_CARD- A credit card number. By default all available card schemes provided by Symfony validator are allowed.CURRENCY- A 3-letter ISO 4217 currency name. Possible example values areUSDorEUR. In edit forms it will be rendered as a currency selector. If the field is notmandatorythe edit selector provides a placeholder entry named All.DATE_INTERVAL- An interval of time which is persisted as a ISO 8601 duration string.HOSTNAME- A host name including a top-level domain. Possible example value:example.com. Special top-level domains reserved in RFC 2606 (.invalid,.localhost, etc.) are excluded.IBAN- A bank account number in IBAN (International Bank Account Number) format.ICON- A Font Awesome icon. An icon selector is provided on edit pages.ISIN- An ISIN (international securities identification number).LANGUAGE- An Unicode language identifier. Possible example values arefrorzh-Hant. A language selector is used in edit pages. For the output in index and detail templates an output modifier is used to display the full name instead of the unreadable language code. If the field is notmandatorythe edit selector provides a placeholder entry named All.LOCALE- A locale. Possible example values arefr(ISO 639-1 code) orfr_FR(ISO 639-1 followed by ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code). The field will be rendered as a locale selector in edit forms. If the field is notmandatorythe edit selector provides a placeholder entry named All.PASSWORD- A password. For this a password input element will be used instead of a normal one in edit pages. Password fields are not shown on index and detail pages for security reasons.PHONE_NUMBER- A telephone number.TIME_ZONE- A time zone. In edit forms such fields will be rendered using a time zone selector.ULID- An ULID (Universally Unique Lexicographically Sortable Identifier).UUID- An UUID (Universally Unique Identifier).WEEK- An ISO 8601 week number. Possible example value is2011-W17. Represented by a week form type.
ISBN style
Represents different ISBN formats to be validated for a string field.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- Default value. Means that the corresponding string field should not represent an ISBN.ISBN10- ISBN-10 code.ISBN13- ISBN-13 code.ALL- Both ISBN-10 and ISBN-13 codes.
ISSN style
Represents different ISSN formats to be validated for a string field.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- Default value. Means that the corresponding string field should not represent an ISSN.NORMAL- Normal ISSN validation, allows lower case x at the end and non hyphenated ISSN values.CASE_SENSITIVE- Requires an upper case X at the end.REQUIRE_HYPHEN- Requires a hyphenated ISSN value.STRICT- CombinesCASE_SENSITIVEandREQUIRE_HYPHEN.
Ip address scope
Represents different ways how to validate a given IP address.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- Default value. Means that the corresponding string field should not represent an IP address.IP4- Validates for IPv4 addresses in all ranges.IP6- Validates for IPv6 addresses in all ranges.ALL- Validates all IP formats in all ranges.IP4_NO_PRIV- Validates for IPv4 addresses without private ranges.IP6_NO_PRIV- Validates for IPv6 addresses without private ranges.ALL_NO_PRIV- Validates all IP formats without private ranges.IP4_NO_RES- Validates for IPv4 addresses without reserved ranges.IP6_NO_RES- Validates for IPv6 addresses without reserved ranges.ALL_NO_RES- Validates all IP formats without reserved ranges.IP4_PUBLIC- Validates for IPv4 addresses using only public ranges (without private and reserved ranges).IP6_PUBLIC- Validates for IPv6 addresses using only public ranges (without private and reserved ranges).ALL_PUBLIC- Validates all IP formats using only public ranges (without private and reserved ranges).
Entity ipTraceable type
Represents different events for triggering the IpTraceable extension.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- No IpTraceable extension (default).UPDATE- On update.CREATE- On create.CHANGE- On property change.
The generator transforms these values to the corresponding implementation as is. There are no differences made between the different ipTraceable types. So beside the actual entity class there won’t be any code parts affected based on which ipTraceable type you use.
Text field
Represents a field type for storing larger text.
A text field has the following properties in addition to the common abstract string field settings:
- length - The length of this field. Default value is
2000. - role - Allows to define a semantic role for this field. Default value is
PLAIN. The available options are explained below.
Text role
Represents different semantic roles a text field can have.
Can be one of the following options:
PLAIN- Default value. Means that the corresponding text field just represents a string without special semantic.HTML- A text containing HTML tags.WYSIWYG- A text containing HTML tags with WYSIWYG editor support.CODE_CSS- A text containing CSS code.CODE_DOCKERFILE- A text containing a Dockerfile.CODE_JS- A text containing JavaScript code.CODE_MARKDOWN- A text containing Markdown code.CODE_NGINX- A text containing NGINX configuration.CODE_PHP- A text containing PHP code.CODE_SHELL- A text containing shell script.CODE_SQL- A text containing SQL code.CODE_TWIG- A text containing Twig template code.CODE_XML- A text containing XML code.CODE_YAML- A text containing YAML code.CODE_YAML_FM- A text containing YAML frontmatter code.
User field
Extension of abstract integer field for storing user identifiers.
An user field has the following properties in addition to the common abstract integer field settings:
- blameable - Which blameable type is used. Default value is
NONE. - blameableChangeTriggerField - Optional name of field to use as change trigger (if type is
CHANGE. Can also beworkflowStateor the name of an incoming relation (syntaxsourceAlias.field). - blameableChangeTriggerValue - Optional value of field to use as change trigger (if type is
CHANGE). - onAccountDeletion - Controls how an application should change the field when users are deleted. Default value is
GUEST. The available options are listed here.
In edit pages the generator will implement an auto completion element allowing searching users by their name. For the output in index and detail templates the user name is shown and linked to the corresponding user profile in case a profile bundle has been set in the Users bundle configuration.
Entity blameable type
Represents different events for triggering the Blameable extension.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- No Blameable extension (default).UPDATE- On update.CREATE- On create.CHANGE- On property change.
The generator transforms these values to the corresponding implementation as is. There are no differences made between the different blameable types. So beside the actual entity class there won’t be any code parts affected based on which blameable type you use.
Email field
Represents a field type for storing email addresses.
An email field has the following properties in addition to the common abstract string field settings:
- length - The length of this field. Default value is
255. - validationMode - Defines the pattern the email address is validated against. Valid values are shown here. Default value is
HTML5.
In edit pages the generator will use email input elements as well as validation on client and server side. For the output in index and detail pages an icon will be shown linking the email address.
Email validation mode
Represents different pattern an email address is validated against.
Can be one of the following options:
LOOSE- A simple regular expression. Allows all values with an “@” symbol in, and a “.” in the second host part of the email address.STRICT- Uses the egulias/email-validator library to perform an RFC compliant validation.HTML5- This matches the pattern used for the HTML5 email input element.
Url field
Represents a field type for storing urls.
An url field has the following properties in addition to the common abstract string field settings:
- length - The length of this field. Default value is
255.
In edit pages the generator will use url input elements as well as validation on client and server side. For the output in index and detail pages an icon will be shown linking the url.
Upload field
Represents a field type for storing upload files.
An upload field has the following properties in addition to the common abstract string field settings:
- allowedExtensions - List of file extensions to be accepted during the upload, separated by a comma with a space char. Default value is
gif, jpeg, jpg, png. If you want to allow all extensions, just use*. - length - The length of this field. Default value is
255. - maxSize - A string for a maximum file size. Default is an empty string for no limit. Examples:
4096(bytes),200k(kilobytes),2M(megabytes),32Ki(kikibytes),8Mi(mebibytes). Read more about that here. - mimeTypes - A string containing a comma separated list of allowed mime types. Default is
image/*. Example:application/pdf, application/x-pdf. If you want to allow all mime types, just use*. - multiple - A boolean specifying whether this field allows multiple files or not. Default value is
false. Note the UI has not been completely adapted for this yet (see #123). - namingScheme - Defines how uploaded files are named. Default value is
ORIGINALWITHCOUNTER. - subFolderName - Name of sub folder for storing uploaded files. If this is empty (default) the field name will be used as folder name.
Image-specific settings (use only if you did not change allowedExtensions):
- minWidth - An integer for a minimum width. Default is
0for no constraint. If set, the width of the image file must be greater than or equal to this value in pixels. - maxWidth - An integer for a maximum width. Default is
0for no constraint. If set, the width of the image file must be less than or equal to this value in pixels. - minHeight - An integer for a minimum height. Default is
0for no constraint. If set, the height of the image file must be greater than or equal to this value in pixels. - maxHeight - An integer for a maximum height. Default is
0for no constraint. If set, the height of the image file must be less than or equal to this value in pixels. - minPixels - An integer for a minimum amount of pixels. Default is
0for no constraint. If set, the image’s amount of pixels must be greater than or equal to this value. - maxPixels - An integer for a maximum amount of pixels. Default is
0for no constraint. If set, the image’s amount of pixels must be less than or equal to this value. - minRatio - A float for a minimum aspect ratio (width / height). Default is
0.00for no constraint. If set, the aspect ratio of the image file must be greater than or equal to this value. If you for example want to ensure that only images are accepted which have a 16:9 format (like a width of 640 pixels and a height of 360 pixels) set bothminRatioandmaxRatioto1.77. - maxRatio - A float for a maximum aspect ratio (width / height). Default is
0.00for no constraint. If set, the aspect ratio of the image file must be less than or equal to this value. If you for example want to ensure that only images are accepted which have a 16:9 format (like a width of 640 pixels and a height of 360 pixels) set bothminRatioandmaxRatioto1.77. - allowSquare - A boolean specifying whether square dimension is allowed or not. Default value is
true. If this option isfalse, the image cannot be a square. If you want to force a square image, then setallowLandscapeandallowPortraitboth tofalse. - allowLandscape - A boolean specifying whether landscape dimension is allowed or not. Default value is
true. If this option isfalse, the image cannot be landscape oriented. - allowPortrait - A boolean specifying whether portrait dimension is allowed or not. Default value is
true. If this option isfalse, the image cannot be portrait oriented. - detectCorrupted - A boolean specifying whether image content is validated or not. Default value is
false. If this option istrue, the image content is validated to ensure that the image is not corrupted. This validation is done with PHP’s imagecreatefromstring function, which requires the PHP GD extension to be enabled.
In edit pages the generator will use upload input elements. If a field is mandatory the upload will be required when creating a new entity, but not when editing an existing one. If a field is optional (not mandatory) then it will be possible to delete existing uploads on editing.
For the output in index and detail pages a download link is shown together with the file size. If the file is an image then a small version of it is shown instead of a text link (on edit pages too by the way).
If an application has any upload fields the generator creates an additional helper class containing methods for image processing. The generated application uses it to determine arguments for creating thumbnail preview images on demand with the help of the Imagine library. Generated applications use the LiipImagineBundle which also provides a Twig extension for generating and embedding thumbnails.
For upload fields with images there are additional settings generated at the configuration page. These allow enabling automatic shrinking of too large images down to configurable maximum dimensions.
For every upload field foo there will be another array field created which is named fooMeta. This field stores some meta information about the uploaded files for convenience, like the file size, the image format (portrait, landscape, square) and the image dimensions. Also EXIF data is saved in this array.
Also for every upload field foo there exists another field named fooUrl which can be used for linking or embedding the original file in an absolute way which works also if short urls point to a virtual subfolder.
Upload naming scheme
Represents different schemes for naming uploaded files.
Can be one of the following options:
ORIGINALWITHCOUNTER- Keep the original file name. Add a counter suffix if required to avoid duplicated file names.RANDOMCHECKSUM- Use a random checksum. This results in quite cryptic filenames.FIELDNAMEWITHCOUNTER- Use the field name as a prefix together with a counter. For exampleimage1,image2, and so on.USERDEFINEDWITHCOUNTER- Let the user optionally define a custom file name. Falls back toORIGINALWITHCOUNTER.
Within the generated upload helper class one of those strategies will be selected depending on the currently treated upload field.
List field
Represents a field type for realising a selection of list values.
A list field has the following properties in addition to the common abstract string field settings:
- expanded - A boolean to enable radio buttons (for single-valued lists) or checkboxes (for multi-valued lists) instead of a select field. The default value is
false. - length - The length of this field. Default value is
255. - multiple - A boolean specifying whether multiple items can be selected concurrently or not. The default value is
false. - min - Minimum amount of values enforced to be selected (only if
multipleis set totrue). The default value is0. - max - Maximum amount of values enforced to be selected (only if
multipleis set totrue). The default value is0. - useAutoCompletion - Enable to create an auto completion field instead of a normal form field (dropdowns, checkboxes, radio buttons). The default value is
false.
A list field may have the following references:
- items - Allows referencing one or more items.
The generator creates an additional class for handling the available list items centrally. Based on this information edit pages provide either a drop-down list (for single or multiple values depending on the multiple property), radio buttons (if multiple is set to false and expanded is set to true) or a checkbox list (if multiple and expanded are both set to true). For the output in index and detail templates there is a filter generated which cares for showing the names instead of the raw option values.
List field item
Represents an entry for a list field.
It includes the following properties:
- default - A boolean specifying whether this entry is selected by default or not. The default value is
false. - image - Optional name of a font awesome icon without
fa-prefix, for examplepencil. - name - Name of the item.
- value - The value of this item. If not value exists, the name is used as value, too.
See the list field section for a description of what the generator does with those elements.
Array field
Represents a field type for storing arrays.
An array field has the following properties in addition to the common derived field settings:
- arrayType - Which array type is used. Default value is
JSON. - min - Minimum amount of items enforced to be present. The default value is
0. - max - Maximum amount of items enforced to be present. The default value is
0which means that no certain amount is enforced.
The generator will exclude arrays for the output in index templates. For edit pages and detail templates there is a simple implementation provided which might be sufficient for flat (non-nested) arrays though.
Datetime field
Represents a field type for storing either datetime values with the format YYYY-MM-DD H:i:s or date values with the format YYYY-MM-DD or time values with the format H:i:s.
A datetime field has the following properties in addition to the common derived field settings:
- components - Which date/time components are activated. Default value is
DATE_TIME. - future - A boolean specifying whether the value must be in the future or not. Default value is
false. - immutable - A boolean specifying whether the value is immutable or not. Default value is
false. If set to trueDateTimeImmutableis used instead ofDateTime. - past - A boolean specifying whether the value must be in the past or not. Default value is
false. - startDate - A boolean specifying whether this field should be treated as a start date. Default value is
false. If set totruethis field is included into determining public visibility of the corresponding objects. - endDate - A boolean specifying whether this field should be treated as an end date. Default value is
false. If set totruethis field is included into determining public visibility of the corresponding objects. - timestampable - Which timestampable type is used. Default value is
NONE. - timestampableChangeTriggerField - Optional name of field to use as change trigger (if type is
CHANGE. Can also beworkflowStateor the name of an incoming relation (syntaxsourceAlias.field). - timestampableChangeTriggerValue - Optional value of field to use as change trigger (if type is
CHANGE). - validatorAddition - Additional validation constraint without the
Assertannotation. Example values areLessThanOrEqual("+15 minutes")orLessThan("-18 years UTC")orRange(min = "first day of January", max = "first day of January next year"). For more details information see this blog post.
Note you can also use now as default value for date and time fields which results in that always the current timestamp is used for setting the initial value.
The past and future properties are implemented as client-side and server-side validators.
The generator will treat input values as date and/or time input elements in edit pages. For the output in index and detail templates a modifier is used to format the value according to the current locale.
DateTime components
Represents different types of date and time fields.
Can be one of the following options:
DATE_TIME- Field stores date with time (default).DATE_TIME_TZ- Field stores date with time and time zone.DATE- Field stores date only.TIME- Field stores time only.
Entity identifier strategy
Represents different strategies for identifier generation.
Can be one of the following options:
AUTO- Choose automatically betweenSEQUENCEandIDENTITY.SEQUENCE- Uses a database sequence.IDENTITY- Uses special identity columns (auto_increment).NONE- No explicit strategy.UUID- Generates universally unique identifiers.ULID- Generates universally unique lexicographically sortable identifiers.CUSTOM- Custom strategy.
The generator transforms these values to the corresponding implementation as is (see Doctrine docs). There are no differences made between the different strategies. So beside the actual entity class there won’t be any code parts affected based on which identifier strategy you use. For UUID and ULID the Symfony UID component is utilized - like shown in the docs (for UUID and ULID).
Entity change tracking policy
Represents different policies defining how changes are determined.
Can be one of the following options:
DEFERRED_IMPLICIT- Compare properties during commit (default). Convenient, but not good for performance.DEFERRED_EXPLICIT- Scan only entities marked for change detection. Better performance, but no dirty checking.
The generator transforms these values to the corresponding implementation as is.
Entity lock type
Represents different locking strategies for entities.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- No locking support.OPTIMISTIC- Optimistic locking.PESSIMISTIC_READ- Pessimistic read locking.PESSIMISTIC_WRITE- Pessimistic write locking.
The generator transforms these values to the corresponding implementation as is. If you use optimistic locking the entity needs an integer with version set to true.
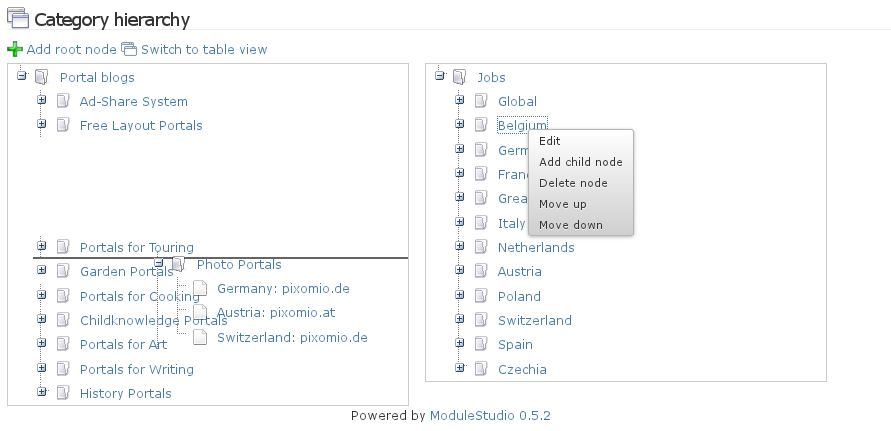
Entity tree type
Represents different tree strategies for entities (see Tree extension for more details).
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- No tree (default).NESTED- Nested set.CLOSURE- Closure.
If an entity has a tree type other than NONE then the generator creates several additional artifacts, like for example:
- An additional template for managing the tree in a hierarchy view.
- An additional view plug-in for creating markup for jsTree.
- An additional template included in detail pages for showing different types of relatives (parents, children, and so on).
- Some ajax functions used by the hierarchy view.
- For closure: separate classes for the closure entities.
Entity slug style
Represents different slug styles for the creation of permalinks.
Can be one of the following options:
LOWERCASE- Lowercase (default).UPPERCASE- Uppercase.CAMEL- Camelcase.
The generator transforms these values to the corresponding implementation as is. There are no differences made between the different slug styles. So beside the actual entity class there won’t be any code parts affected based on which slug style you use.
Array type
Represents different types of arrays used by Doctrine 2.
Can be one of the following options:
JSON- A JSON array (default).SIMPLE_ARRAY- A simple array represented by a comma-separated text field.
The generator transforms these values to the corresponding implementation as is. There are no differences made between the different array field types. So beside the actual entity class there won’t be any code parts affected based on which array type you use.
Entity timestampable type
Represents different events for triggering the Timestampable extension.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- No Timestampable extension (default).UPDATE- On update.CREATE- On create.CHANGE- On property change.
The generator transforms these values to the corresponding implementation as is. There are no differences made between the different timestampable types. So beside the actual entity class there won’t be any code parts affected based on which timestampable type you use.
Account deletion handler
Represents the kind of reaction to perform if users are deleted, but still referenced in some data of the generated application.
Can be one of the following options:
ADMIN- Sets the corresponding user id to2(admin user).GUEST- Sets the corresponding user id to1(guest).DELETE- Deletes the entity.
Entity index
Represents an entity index.
It includes the following properties:
- type - The index type (see below.
An index may have the following references:
- entity - Reference to the owning entity.
- items - Allows referencing one or more index items.
Entity index type
Represents different types of entity indexes.
Can be one of the following options:
NORMAL- Normal index (default).UNIQUE- Index with unique constraint.FULLTEXT- Fulltext index.
The generator transforms these values to the corresponding implementation as is. There are no differences made between the different index types. So beside the actual entity class there won’t be any code parts affected based on which index type you use.
Entity index item
Represents a part of an index, referencing to an equally-named field.
An index item may have the following references:
- index - Reference to the owning element.
Relationship
Base class for all types of associations between entities.
A relationship may have the following references:
- application - Reference to the owning element.
- source - Allows referencing a target data object.
- sourceAlias - The alias for the source entity, required to have multiple associations between the same entities. The name should reflect the cardinality on the source side (singular or plural forms) depending on the relationship type. As with all names camel case is preferred, for example
personAddresses. - target - Allows referencing a source data object.
- targetAlias - The alias for the target entity, required to have multiple associations between the same entities. The name should reflect the cardinality on the target side (singular or plural forms) depending on the relationship type. As with all names camel case is preferred, for example
personAddresses.
Join relationship
Collects all foreign key and join relationships.
It includes the following properties in addition to the common relationship settings:
- cascade - The cascade type used on application level from source view. The default value is
NONE. - cascadeReverse - The cascade type used on application level from target view (only for
bidirectionalrelationships). The default value isNONE. - expandedSource - A boolean to enable usage of radio buttons (for single-valued relations) or checkboxes (for multi-valued relations) instead of a select field. The default value is
false. - expandedTarget - A boolean to enable usage of radio buttons (for single-valued relations) or checkboxes (for multi-valued relations) instead of a select field. The default value is
false. - fetchType - The fetch type for this association. The default value is
LAZY. - nullable - A boolean specifying whether the field for this relationship may be null or not. The Default value is
true. - onDelete - String for optional delete cascade options on database level (for example
RESTRICTorSETNULL). - sourceEditing - The edit mode for target elements during editing the source side of this association. The default value is
CHOOSEfor many to one as well as many to many relationships andNONEfor other join relationships. - sourceField - Name of the source entity field(s) used for the join. The default value is
idwhich means that the source entity is joined by it’s primary key. It is possible to change that value for custom join conditions. Furthermore it is possible to use multiple field names separated by a comma with a space char in order to join entities with multiple keys. - targetEditing - The edit mode for source elements during editing the target side of this association. The default value is
NONEfor many to many relationships andCHOOSEfor other join relationships. - targetField - Name of the target entity field(s) used for the join. The default value is
idwhich means that the target entity is joined by it’s primary key. It is possible to change that value for custom join conditions. Furthermore it is possible to use multiple field names separated by a comma with a space char in order to join entities with multiple keys. - unique - A boolean specifying whether the field for this relationship is unique or not. The default value is
false. - useAutoCompletion - If set to any value except
NONEthe generator will create an auto completion field instead of a normal form field (dropdowns, checkboxes, radio buttons) for the corresponding side(s) of the relationship. For more information see the available options.
The generator transforms most of these settings to the corresponding implementation as is. The only thing which is used outside of the entity classes are the edit mode and auto completion usage which control how relationships are handled in edit actions.
Join relationships are automatically incorporated into the DQL queries which are placed in the entity repository classes. You can override these methods for changing selection details if required.
One to one relationship
Represents one-to-one relationships.
It includes the following properties in addition to the common join relationship settings:
- bidirectional - A boolean specifying whether this relationship is bidirectional or not. The default value is
false. - inheritPermissions - A boolean specifying whether the source visibility should affect the target visibility or not (only for
bidirectionalrelationships). The default value isfalse. If set totruethe target can only be accessed if normal permissions are given and access to the source is also granted. - orphanRemoval - Default value is
false. If set totrueorphans get removed automatically. - primaryKey - A boolean specifying whether the foreign key of this relation should act as a primary key. The default value is
false. Please note that this has not been tested yet and probably won’t be supported properly yet by the controller layers in the generated application.
One to many relationship
Represents one-to-many relationships.
It includes the following properties in addition to the common join relationship settings:
- bidirectional - A boolean specifying whether this relationship is bidirectional or not. The default value is
false. - indexBy - Set to target field name (must be unique) to specify the index by criteria for the relation. Please note that this has not be tested very well yet. More information can be found in this article.
- inheritPermissions - A boolean specifying whether the source visibility should affect the target visibility or not (only for
bidirectionalrelationships). The default value isfalse. If set totruethe target can only be accessed if normal permissions are given and access to the source is also granted. - orderBy - Set to target field name(s) to specify the sorting criteria for the outgoing relation. Some examples are shown below.
- orphanRemoval - Default value is
false. If set totrueorphans get removed automatically. - minTarget - Minimum amount of items enforced to be present on the target side. The default value is
0. - maxTarget - Maximum amount of items enforced to be present on the target side. The default value is
0which means that no certain amount is enforced.
Many to one relationship
Represents many-to-one relationships.
It includes the following properties in addition to the common join relationship settings:
- primaryKey - A boolean specifying whether the foreign key of this relation should act as a primary key. The default value is
false. Please note that this has not been tested yet and probably won’t be supported properly yet by the controller layers in the generated application. - sortableGroup - A boolean specifying whether the foreign key of this relation acts as grouping criteria for the Sortable extension. The default value is
false.
Many to many relationship
Represents many-to-many relationships.
It includes the following properties in addition to the common join relationship settings:
- bidirectional - A boolean specifying whether this relationship is bidirectional or not. The default value is
false. - indexBy - Set to target field name (must be unique) to specify the index by criteria for the relation. Please note that this has not be tested very well yet. More information can be found in this article.
- inheritPermissions - The permission inheritance type specifying whether and how the source visibility should affect the target visibility (only for
bidirectionalrelationships). The default value isNONE. - orderBy - Set to target field name(s) to specify the sorting criteria for the outgoing relation. Some examples are shown below.
- orderByReverse - Set to source field name(s) to specify the sorting criteria for the incoming relation. Some examples are shown below.
- orphanRemoval - Default value is
false. If set totrueorphans get removed automatically. - refClass - Specifies the reference class created for the linking table (for example
personAddress). The generator creates additional classes for this reference-managing entity. - minSource - Minimum amount of items enforced to be present on the source side. The default value is
0. - maxSource - Maximum amount of items enforced to be present on the source side. The default value is
0which means that no certain amount is enforced. - minTarget - Minimum amount of items enforced to be present on the target side. The default value is
0. - maxTarget - Maximum amount of items enforced to be present on the target side. The default value is
0which means that no certain amount is enforced.
Cascade type
Represents different cascade types on application level.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE(default)PERSISTREMOVEMERGEDETACHPERSIST_REMOVEPERSIST_MERGEPERSIST_DETACHREMOVE_MERGEREMOVE_DETACHMERGE_DETACHPERSIST_REMOVE_MERGEPERSIST_REMOVE_DETACHPERSIST_MERGE_DETACHALL
The cascade type is implemented as defined in the association’s annotation within the corresponding entity classes. At the moment there are no other code parts depending on that.
Ordering many valued relationship sides
As shown in the Doctrine documentation an OrderBy annotation can be used to specify an implicit sorting criteria which will be appended to DQL queries.
Fields are used with their unqualified names and must exist in the referenced source or target entity. If the referenced entity uses the geographical extension you can also use latitude and longitude. If it uses the standardFields extension you can also use createdDate, createdBy, updatedDate and updatedBy.
ModuleStudio offers different syntax variants for using this for single and multiple fields:
- Order by a single field:
mySortField - Order by a single field with direction:
mySortField:descormySortField:DESC - Order by multiple fields:
lastName, firstName - Order by multiple fields with direction:
score:desc, lastName:ascorscore:DESC, lastName
The sorting direction is optional and defaults to ASC.
Many to many permission inheritance type
Defines whether and how the source visibility should affect the target visibility (only for bidirectional many to many relationships).
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- Use no permission inheritance (default). The target can be accessed if normal permissions are given.AFFIRMATIVE- The target can only be accessed if normal permissions are given and access to at least one source is also granted.UNANIMOUS- The target can only be accessed if normal permissions are given and access to all sources is also granted.
Auto completion usage
Defines whether and which sides of a relationship will be handled by an auto completion field instead of normal form fields (dropdowns, checkboxes, radio buttons) during editing.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- Use no auto completion.ONLY_SOURCE_SIDE- Use auto completion when selecting entities of the source side (editing of the target side).ONLY_TARGET_SIDE- Use auto completion when selecting entities of the target side (editing of the source side).BOTH_SIDES- Use auto completion on both sides.
Relation fetch type
Represents different fetch types for join relationships.
Can be one of the following options:
LAZY- Lazy (default).EAGER- Eager.EXTRA_LAZY- Extra lazy.
The generator transforms these values to the corresponding implementation. There are no differences made yet between the different fetch types as the generator uses DQL for almost all selections. So beside the actual entity class there won’t be any code parts affected based on which fetch type you use.
Relation edit mode
Represents different edit modes for each side of join relationships.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- Editing the other side does nothing regarding elements from this side.CHOOSE- Editing the other side includes choosing elements from this side.INLINE- Editing the other side includes choosing, creating and editing elements from this side.EMBEDDED- Editing the other side allows embedded creation and editing of an element from this side.
For each entity the generator creates some templates to be included in the edit templates of related entities (for example a detail list and another one for edit). Depending on which edit mode is defined for a relationship the corresponding edit template (choose or edit) is included or not.
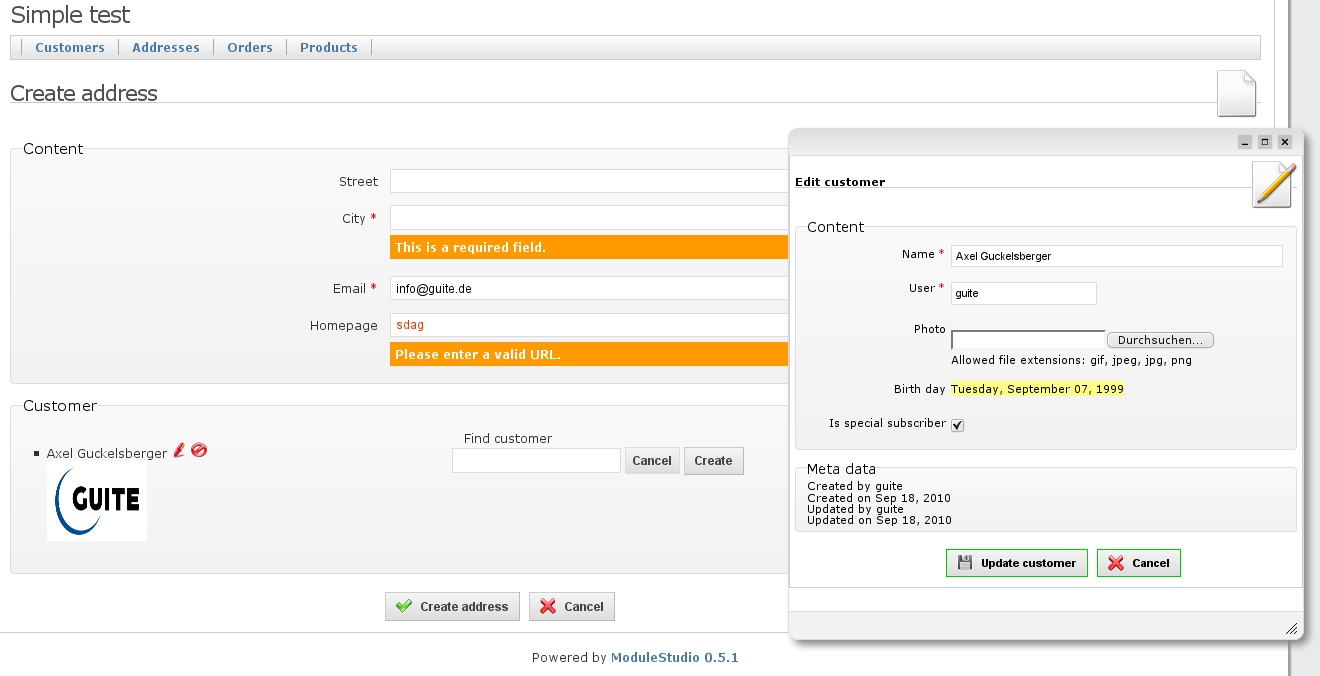
NONEmeans that there is no possibility to take influence on the association.CHOOSEmeans that it is possible to select a related entity (using dropdowns, radio buttons, checkboxes or auto completion).INLINEmeans the same asCHOOSEplus that it is also possible to create and edit related entities during editing the main entity.EMBEDDEDmeans that the edit form for the related entity will be incorporated into the edit form of the main entity.
Example for inline editing:
Embedded editing is limited to single-valued relationship sides at the moment. So you can for example embed editing a category into editing an article, but not multiple categories.
Inheritance relationship
Represents inheritance relationships for describing entity class hierarchies.
It includes the following properties in addition to the common relationship settings:
- discriminatorColumn - Name of the field used for storing the entity type.
- strategy - The inheritance strategy used for data storage. The default value is
SINGLE_TABLE.
Inheritance strategy type
The strategy type defines which kind of inheritance strategy should be used.
Can be one of the following options:
SINGLE_TABLE- Simple inheritance: share everything and store it in the parent table (default).JOINED- Concrete inheritance: each entity stores everything in its own table.
The generator transforms these values to the corresponding implementation. There are no differences made yet between the different strategies. So beside the actual entity class there won’t be any code parts affected based on which strategy you use.
Variables
Container class for carrying bundle variables.
It includes the following properties:
- sortOrder - The sorting position for when using multiple variable sections. Default value is
1.
A var container may have the following references:
- application - Reference to the owning element.
- fields - Allows referencing one or more fields.
The generator creates a bundle configuration for variables. Multiple variable containers can be used to group settings into logical semantic groups.
Controller layer
Language elements
Action
An action represents a controller function which can be called by the user. Zikula uses Symfony routing for that. An action can either be contained in a controller element or in an entity which corresponds to an entity-related controller.
The following action types are available:
- Index action - default function; processes a collection of entities.
- Detail action - shows a certain entity in detail.
- Edit action - an action for editing an entity.
- Delete action - an action for deleting an entity.
- Custom action - for custom actions, like e[mySpecialFunction.
An action may have the following references:
- entity - Reference to the owning entity controller.
The generator creates sensitive default implementations for all action types except custom actions which do only return an empty template.
It is possible to create special versions for all templates by adding a suffix which will be assigned by the tpl parameter. For example you can call detailMyVersion.html.twig by adding &tpl=myVersion to the url. Note this additional override capability is mainly intended for all actions which have a template for each entity and has therefore not been considered for index and custom actions yet.
Index action
An index action implementation offers a generic list view of multiple items which can be sorted and filtered. Also there are alternative template formats created for atom, csv, json, rss, xml and maybe kml support. Just add &userssext=1 to the url or, even easier with shorturls, change persons.html to persons.rss.
Detail action
A detail action results in a generic detail view of an entity. Again there are alternative formats supported, like for example csv, json and xml.
Edit action
The edit implementation creates form pages for changing entities and their relations. Beside the form handler classes this involves form types and corresponding template files.
Note it is possible to change entity form field default values by setting request variables when creating new entities. For example the GET parameter set_xyz=123 sets the entity field xyz to 123 before rendering the form.
Delete action
For a delete action the generator creates the well-known confirmation page asking the user whether he really wants to delete the given entity.
Custom action
A custom action is only created as a mockup which contains the permission check as well as some other stuff which is always required, like returning the output from a template fetched by the view.
Workflow layer
The workflow layer is not very configurable yet. At the moment there are three predefined workflows available which can be defined in the model for each entity.
Entity workflow type
Represents different workflows for entities.
Can be one of the following options:
NONE- No approval (default).STANDARD- Single approval.ENTERPRISE- Double approval.
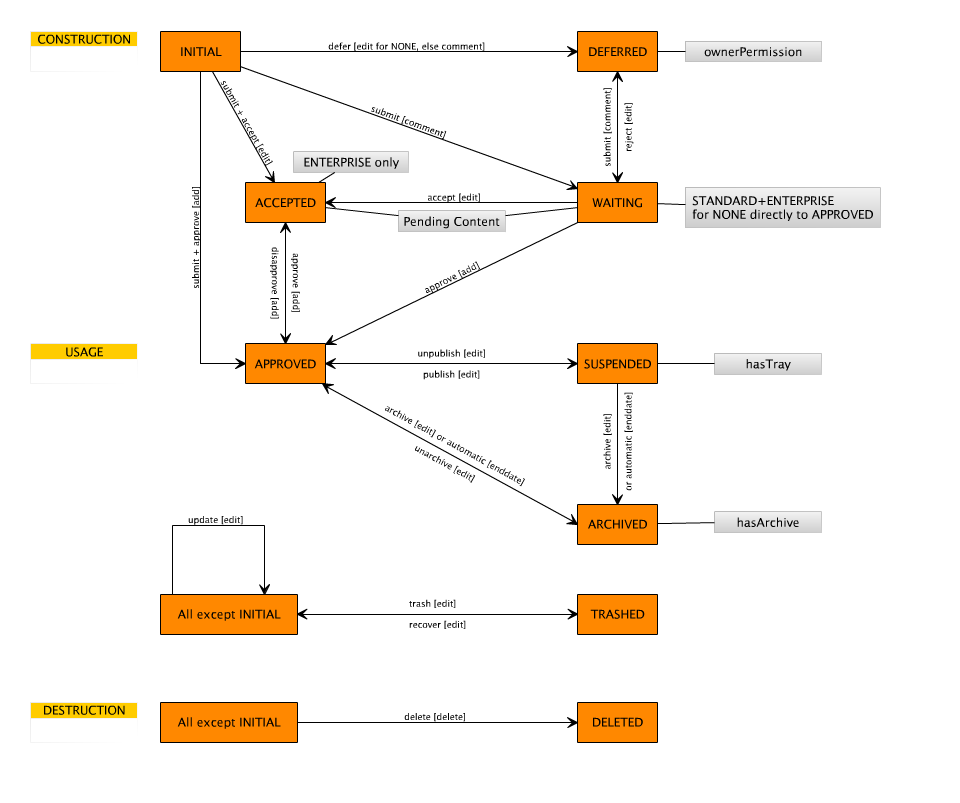
In total there are nine different workflow states which are explained below. Note that you can arrange many states by corresponding properties in the model.
- Initial - pseudo-state for content which is just created and not persisted yet.
- Deferred - content has not been submitted yet or has been waiting, but was rejected. Only available if the entity has set the
ownerPermissionproperty totrue. Allows users to manage their contributions. Otherwise rejected content would be deleted. - Waiting - content has been submitted and waits for approval. Only available for
STANDARDandENTERPRISE. Fetched for moderation panel. - Accepted - content has been submitted and accepted, but still waits for approval. Only available for
ENTERPRISE. Fetched for moderation panel. - Approved - content has been approved and is available online.
- Suspended - content has been approved, but is temporarily offline. Only available if the entity has set the
hasTrayproperty totrue. - Archived - content has reached the end and became archived. Only available if the entity has set the
hasArchiveproperty totrue. Requires a datetime field being designated as end date. - Trashed - content has been marked as deleted, but is still persisted in the database.
- Deleted - pseudo-state for content which has been deleted from the database.
The following image shows an overview of all possible workflow states and actions.
For storing the current state for a certain object ModuleStudio adds an additional field named workflowState to each entity before starting the generation. This can also be used for easy filtering. In fact ModuleStudio adds it as a list field which contains a list field item for each state.
Note that it is easily possible to model date or datetime fields which set their value automatically depending on a certain workflow state. Just set their timestampable type to CHANGE and set workflowState as change trigger field. Also set the change trigger value to the name of the desired state. So you could for example create an approval date by using approved for the trigger value property.
For all entities having another workflow than NONE there are configuration options in the generated configuration page for selecting user groups for moderation. If these settings are not applied, the default group for administrators is used as fallback. With the help of this information, email notifications are sent between creator and moderators on state changes. For moderators there is a textarea field provided in the form for specifying additional remarks, like a reason for deny (particularly useful for reject and demote / disapprove actions).
Workflow customisation
If you need to use a more custom workflow or if you want to let several entities in multiple bundles the same workflow you can do the following:
- You can edit the generated workflow YAML files using a text editor.
- When you are finished you need to save this workflow in
app/Resources/workflows/. - All entities using your custom workflow must not occur in any other workflows. So you need to customize or remove the generated workflow files within the corresponding bundles.